
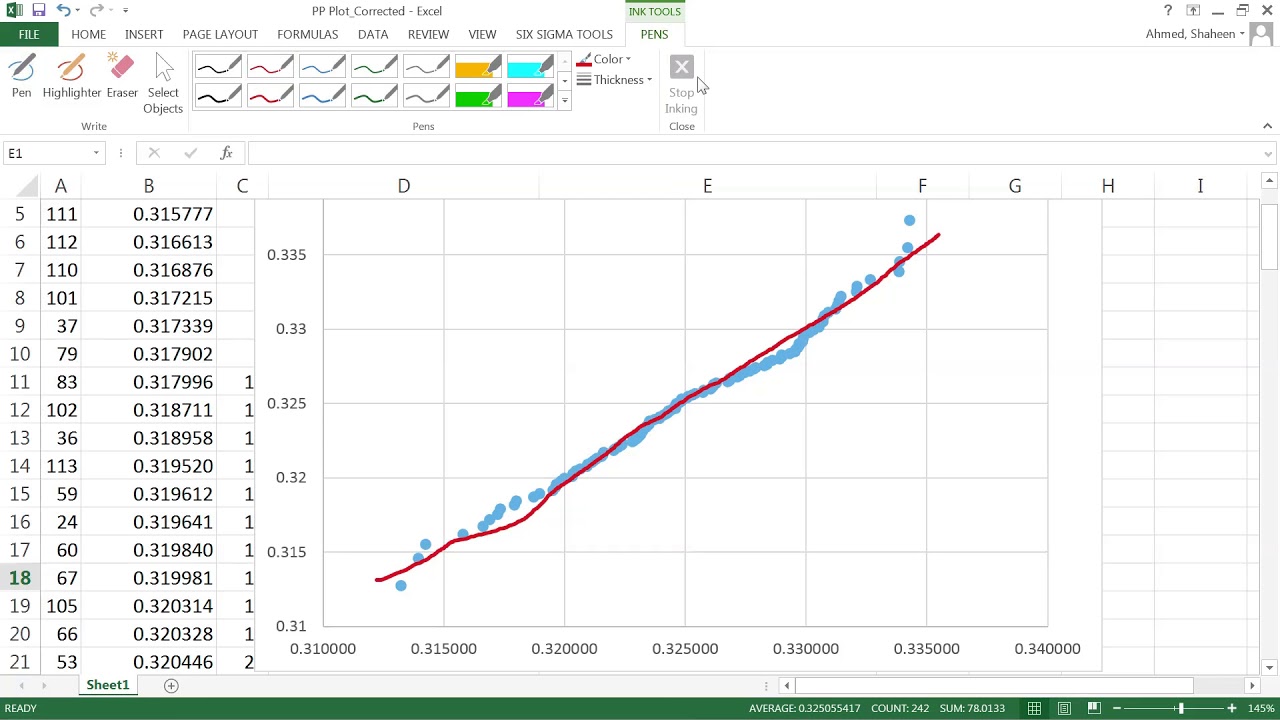
Normal plots are often used with as few as 7 points, e.g., with plotting the effects in a saturated model from a 2-level fractional factorial experiment. With more points, random deviations from a line will be less pronounced. Normally, as with stem and leaf plots and bar charts, we would get Minitab to produce histograms for us, rather than draw them by hand. If the sample has mean 0, standard deviation 1 then a line through 0 with slope 1 could be used. The further the points vary from this line, the greater the indication of departure from normality. As a reference, a straight line can be fit to the points. The first example uses the standard normal distribution (i.e., z distribution), which has a mean of 0 and standard deviation of 1 this is the default when first constructing a probability distribution plot in Minitab. If the data are consistent with a sample from a normal distribution, the points should lie close to a straight line. The following two examples use Minitab to find the area under a normal distribution that is greater than a given value. Z i = Φ − 1 ( i − a n + 1 − 2 a ), Īnd Φ −1 is the standard normal quantile function. The formula used by the "qqnorm" function in the basic "stats" package in R (programming language) is as follows: ĭifferent sources use slightly different approximations for rankits. Calculating Cumulative Probabilities from a Normal Distribution. Some plot the data on the vertical axis others plot the data on the horizontal axis. Each topic has its own page of screenshots. an approximation to the means or medians of the corresponding order statistics see rankit. A 45-degree reference line is also plotted.The normal probability plot is formed by plotting the sorted data vs. A q-q plot is a plot of the quantiles of the first data set against the quantiles of the second data set. The quantile-quantile ( q-q) plot is a graphical technique for determining if two data sets come from populations with a common distribution.

To Create a Normal Probability Plot in Excel Bower, M.S., Technical Training Specialist, Minitab Inc. Similarly, you may ask, how do you create a probability plot in Excel? Left Skew - If the plotted points bend down and to the right of the normal line that indicates a long tail to the left. Similarly, ggplot's statqq () seems to present similar information with a transformed x axis.
#Normal probability plot minitab how to
Unfortunately, I cannot figure out how to add the confidence interval bands around this plot. The probplot gets you most of the way there. Minitab describes this as a normal probability plot. One may also ask, how do you know if a probability plot is skewed? It indicates that your distribution has: Right Skew - If the plotted points appear to bend up and to the left of the normal line that indicates a long tail to the right. I am trying to recreate the following plot with R.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
